What is Pleural Effusion. Edema in lung proper not very mobilePleural fluid is.

Chest X Ray Showing A Moderate Left Pleural Effusion And Subpulmonic Download Scientific Diagram
After watching this video you will know how to search for and identify a pneumothorax.

How to see pleural effusion on x ray. Pleural effusionlateral decubitus view A lateral decubitus chest radiograph with the side containing the pleural effusion placed down dependent demonstrate smaller amounts of free-flowing pleural effusions 1 millimeter of thickness of pleural fluid in. Pseudo-elevation of the diaphragm. When you do see this it is highly specific for a pericardial effusion.
Often a lateral view usually accompanies a PAAP chest X-rayThis can be helpful in settings where the single. Lung cancer can do this also. Forces that influence the appearance of pleural fluid on a chest radiograph depend on the position of the patient the force of gravity the amount of fluid and the degree of elastic recoil of the lung.
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space ie. For pleural effusion of less than 50 ml the x-ray has to be taken in the lying position with the patient turned towards the side of effusion. The fluid may be transude exudate blood chyle or rarely bile.
Effusion and collapse. This condition can be identified by a chest x-ray if the fluid level is more than 300ml. The combination can make the CXR very difficult to interpret.
These conditions are not mutually exclusive. Tap onoff image to showhide findings. The radiological pleura is abnormal if the pleural space becomes visible and the grayscale image is too black too white or too black and too white in combination.
At least 200ml-300 ml of fluid must be present before upright chest films can detect signs of pleural effusion eg. Chest films acquired in the lateral decubitus position with the patient lying on their side are more sensitive and can detect as little as 50 ml of fluid. Chest X-Ray Signs of Pleural Effusion.
Increased density of the affected hemithorax. Infection heart failure cancer inflammatory conditions such as lupus cirrhosis post heart surgery pulmonary embolism clots to the lungs amongst other causes. Comparison of PA vs.
The tests most commonly used to diagnose and evaluate pleural effusion include. Note the larger appearing heart on the AP view. Chest x-ray is a simple test to diagnose pleural effusion see figures 145 and 6.
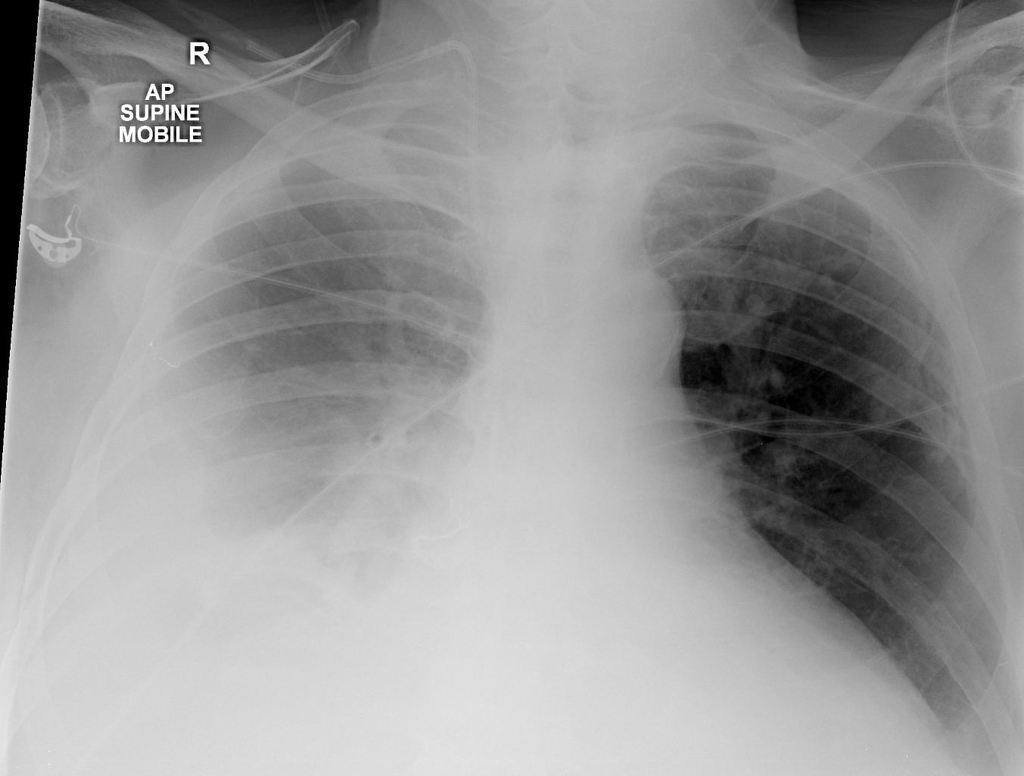
The amount of fluid to be evident on a posteroanterior film is 200 mL whereas costophrenic angle blunting can be appreciated on a lateral film when approximately 50 mL of fluid has accumulated. X-ray chest shows a large pleural effusion on left side the trachea and mediastinum are pushed to the right right lung field is clear. AP views of chest X-rays.
An excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space is known as a pleural effusion. Of course you dont diagnose a pericardial effusion purely on a chest X-ray - if the X-ray is suggestive you order an echocardiogram. At first glance there is clearly white out of the left hemithorax with a meniscus sign.
Pathology making x-rays the most common means of initial diagnosis of this condition 21. Does pleural effusion show on X-ray. A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid in the pleural space an area between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and the chest wall.
This is a common finding on chest X-ray which can have many causes such as. But clinical identification of pleural effusion is possible only when the amount of fluid is more than 500ml. This is because the distance is increased between the film and the heartallowing for the X-rays to spread for a greater distance before developing the film Lateral views rightleft.
Computed tomography CT scan of the chest. This is a more difficult case. A pleural effusion is a collection of fluid in the pleural space.
Specific Radiological Check List. In addition with pleural effusion one can often see a fluid level or signs of fluid tracking around the lung as highlighted by the arrows above. Thoracentesis a needle is inserted between the ribs to remove a biopsy or sample of fluid.
Loss of the costophrenic angle. Loss of lower lobe vessels. Pulmonary edema is fluid that accumulates in interstitial or alveolar spaces of the lungs properPleural fluid will change configuration or move in the pleural space from.
Blunted costophrenic angles. Ultrasound of the chest. If the patient is upright when the X-ray is taken then fluid will surround the lung base forming a meniscus a concave line obscuring the costophrenic angle and part or all of the hemidiaphragm.
Fluid gathers in the lowest part of the chest according to the patients position. An example of frontal x-ray with Pleural E usion is shown in Figure 2. Recognizing the Different Appearances of Pleural Effusions.
Chest X Ray differential diagnosis for pleural effusion - YouTube. Standard posteroanterior and lateral chest radiography remains the most important technique for initial diagnosis of pleural effusion. A pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid between the layers of pleura that cover the lung.
This indicates the presence of a pleural effusion. Ensure trachea is visible and in midline Trachea gets pushed away from abnormality eg pleural effusion or tension pneumothorax. One should barely see the thoracic vertebrae behind the heart Check exposure One needs to be able to identify both costophrenic angles and lung apices.
The pericardial fat pad is indicated on the lateral X-ray by the black arrows. Usually radiologists are able to detect this condition in frontal x-rays from e usions with over 200ml of uid or 50ml in some lateral x-rays10. Chest X-rays can detect pleural effusions which often appear as white areas at the lung base.
This video shows the differential diagnosis of pleural_effusion. It also shows how to differentiate it fromdiaphragmatic. How is pleural effusion diagnosed.
By changing patient position. A - Airway. Hover onoff image to showhide findings.
Diagnosis of Pleural Effusions Chest X-ray. You can see all these features in the X-ray below. We have learned that the pleural spaces are potential space that can accumulate fluid and air.
Commonly pneumonia will present with consolidation and effusion. Between the visceral and parietal layers of pleura.
Pleural Effusion Supine Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pleural Effusion Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pleural Effusion Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Chest X Ray With Small To Moderate Size Right Pleural Effusion Red Download Scientific Diagram

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar